The search results can be filtered or refined using different filters or terms (Figure 1).
The OmicsDI web application supports at the moment nine different refinements: Omics Type, repository/database,
Organisms, Tissue, diseases, Modifications (proteomics), Instruments and platforms, Publication data,
Technology type.
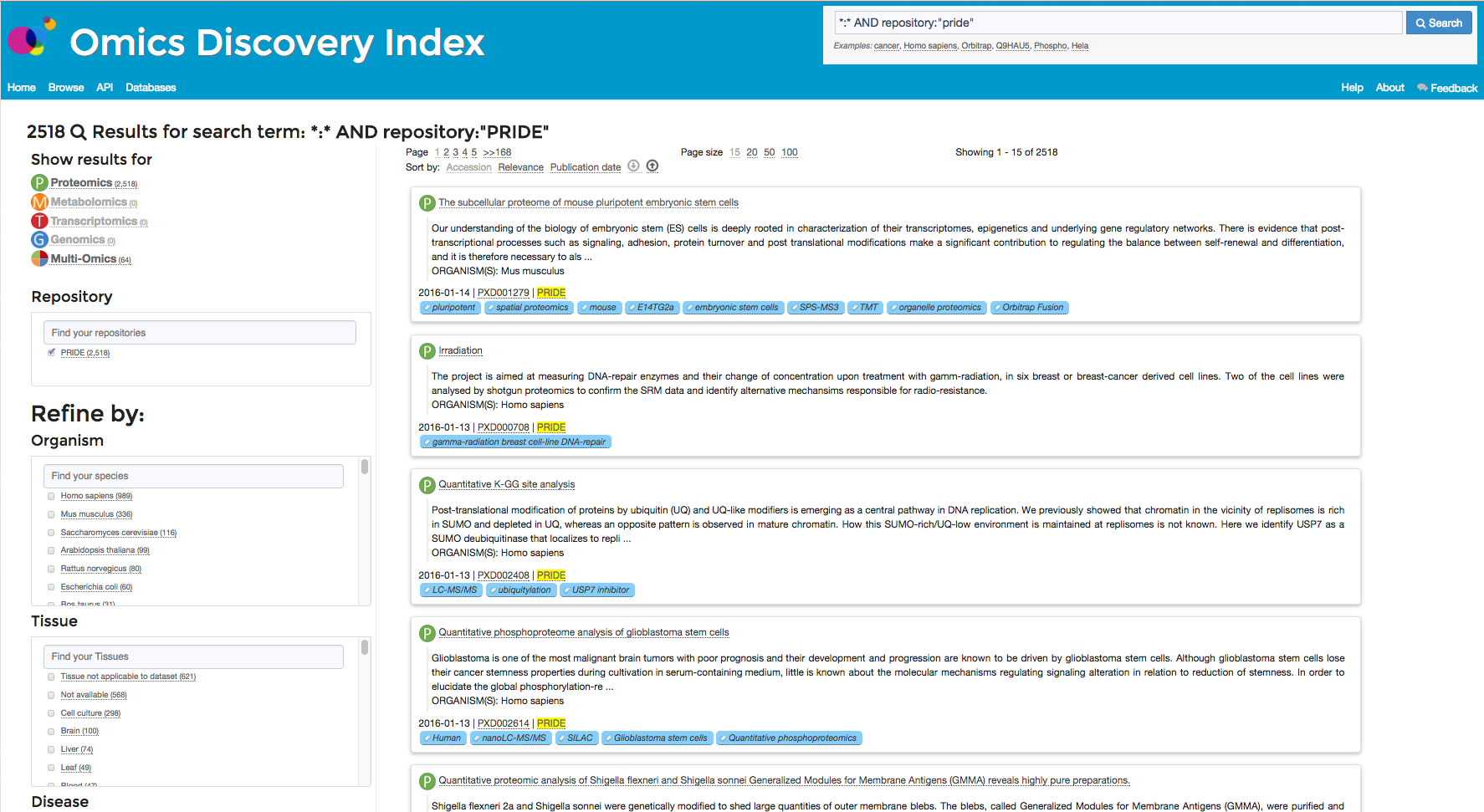
Figure 1: Filtering results of Search in the Browse Page
Filter Box
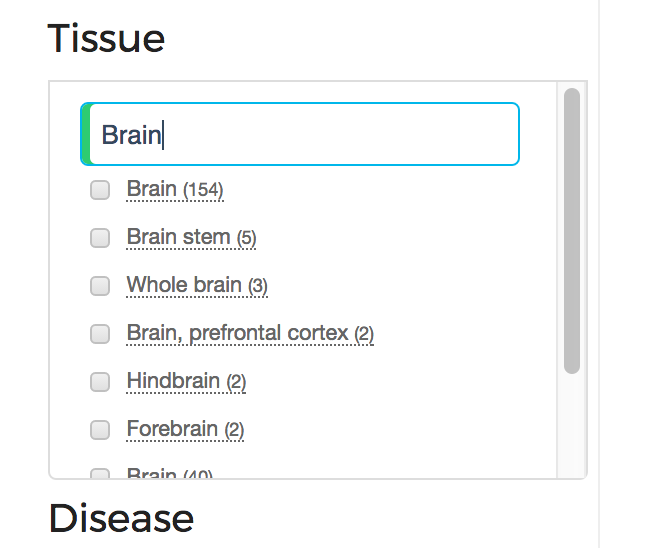
Figure 2: Tissue Filter Box
Each Filter Box shows the number of datasets within each category (e.g tissue type). The user can search in the textfield
for a certain category and the system will filter the categories by the keywords the user specifies. For example (Figure 2), if the user is interested
in brain tissue, then s/he can see all the tissues containing the keyword brain.
Notice that most of the filters are free text based meaning that their values rely on the
annotations provided by the specific databases.
OmicsDI Team is always improving the automatic annotation system to move more attributes/properties of the dataset
from Free-Text to ontology-based values.Ranking Results

Figure 3: Ranking the Search Results
The final results of the search can be sorted by three different categories: Accession, Relevance, Publication Date. The
Accession is the accession of the datasets in the system; the Relevance is how close is the dataset to specific query; the
Publication Date sort the datasets by publication date.
Relevance
The actual search is done via a call to Apache Lucene, which takes two arguments: the query and an upper bound on the number of hits (datasets) to return.
Lucene scoring uses a combination of the Vector Space Model (VSM) of Information Retrieval and the Boolean model to determine how relevant a given Document is to a User's query. In general, the idea behind the VSM is the more times a query term appears in a document relative to the number of times the term appears in all the documents in the collection, the more relevant that document is to the query. It uses the Boolean model to first narrow down the documents that need to be scored based on the use of boolean logic in the Query specification. Lucene also adds some capabilities and refinements onto this model to support boolean and fuzzy searching, but it essentially remains a VSM based system at the heart.